AWS Integration
Zend Server on Amazon is the enterprise way to run PHP in the cloud. An application server with a supported PHP runtime, Zend Server gives PHP developers and DevOps engineers development tools such as Z-Ray, app deployment automation, performance monitoring, request analysis, and configuration management - so apps run faster, scale better, and stay up longer. It is particularly useful for running mobile app back ends that require scalability based on demand.
CloudFormation
Zend Server’s integration with AWS CloudFormation gives you instant access to all of the above, by effortlessly provisioning and setting up an auto-generated CloudFormation template, which includes Zend Server, a database and a load balancer.
Automated scaling of your server deployment guarantees effective handling of web traffic fluctuations. As load increases, additional server instances are automatically added to your server deployment. In case of a decrease in load, deployment is automatically scaled down. To ensure high availability at the application level, user sessions are always maintained on multiple server instances.
User Data
When you manually launch a Zend Server instance on AWS you have the option of passing user data to the instance that can be used to perform common automated configuration tasks and even run scripts after the instance starts. For more information, see AWS User Data.
Getting Support:
For a breakdown of the available Zend Server service level agreements, see http://www.zend.com/support-center/support/production-sla
To streamline the support process, register with Zend at http://www.zend.com/go/amazon-support-registration
Getting Started with Zend Server on AWS
|
|
|
Zend Server Integration with AWS CloudFormation
|
|
|
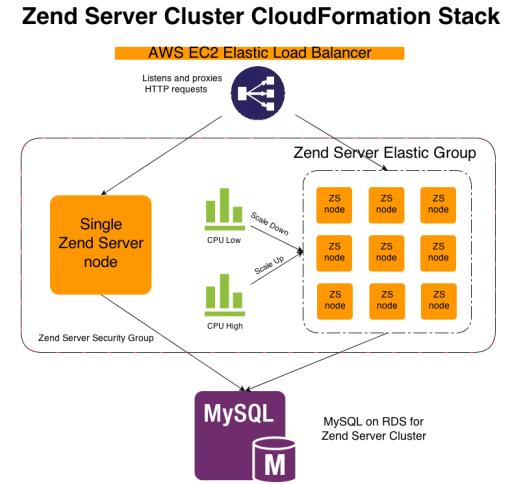
Scaling Up
In case of an increase in traffic load, CloudFormation and the Zend Server cluster will automatically add instances to the deployment, apply cluster configurations, and deploy applications:
- The High CloudWatch alarm identifies an average high CPU usage for the Zend Server instances in the Elastic Group of over 90%.
- A notification is sent to the operator email defined in the template, reporting the status, and the Scaling Policy is triggered to scale up the Elastic Group.
- The Elastic Group scales up by starting a new Zend Server instance.
- The new Zend Server instance receives cluster PHP and system configurations according to teh blueprint existing on the MySQL database.
- All deployed applications in the cluster are deployed on the new Zend Server instance.
- The new instance is added to the Elastic Load Balancer.
Scaling Down
If there is a decrease in traffic load, CloudFormation and the Zend Server cluster will automatically handle the scaling down of the deployment and ensure high availability with a graceful shutdown of instances:
- The Low CloudWatch alarm identifies an average low CPU usage for the Zend Server instances in the Elastic Group of below 30%
- A notification is sent to the operator email defined in the template, reporting the status, and the Scaling Policy is triggered to scale down the Elastic Group
- A Zend Server instance in the Elastic Group is stopped
Note:
Instances can also be manually removed from the server deployment using the AWS Management Console, though this not recommended.
- During shutdown of the Zend Server instance, it is removed from the cluster while migrating sessions in Session Clustering
- The Zend Server instance is removed from the Elastic Load Balancer
Get acquainted with basic AWS concepts:
| Term | Description |
|
Amazon Machine Image (AMI) |
A template that contains a software configuration (for example, an operating system, an application server, and applications). From an AMI, you launch instances, which are copies of the AMI running as virtual servers in the cloud. You can launch multiple instances of an AMI, as shown in the following figure. |
|
Instance |
Amazon EC2 Instances are virtual servers that can run applications that are created from an AMI and after selecting an appropriate instance type. Instance types comprise varying combinations of CPU, memory, storage, and networking capacity and give you the flexibility to choose the appropriate mix of resources for your applications. Each instance type includes one or more instance sizes, allowing you to scale your resources to the requirements of your target workload. |
|
CloudFormation |
AWS CloudFormation gives developers and systems administrators an easy way to create and manage a collection of related AWS resources, provisioning and updating them in an orderly and predictable fashion. |
|
CloudFormation Template |
A CloudFormation template includes pre-configured software instances for quick deployment on EC2. Once deployed, templates can be configured, removed, or re-deployed using the AWS Management Console, through the AWS CloudFormation command line tools or via the AWS CloudFormation APIs. You can deploy and update a template and its associated collection of resources (called a stack) via the AWS Management Console, CloudFormation command line tools or APIs. |
|
AWS Management Console |
The AWS Management Console provides a simple web interface for using Amazon Web Services. Log in using your AWS account name and password. |

